In classic text searches we provide a query and it returns a list of potential matches ordered by relevance. Visually you are able to select the one you want. Voice search technologies work differently.
How does voice searches work?
When users engage with a voice application from a voice-first platform such as Google Assistant or Amazon Alexa, they state what they need and the platform figures out how to accomplish it.
It is not possible to pick the answer you are looking for from a list of results. The voice assistant will select the best answer for you.
This imposes some new challenges to businesses that want to stay relevant in these new platforms.
Different type of queries or invocations
A query can also be called invocation. At the end of the day, you are asking for a voice application that is going to resolve your need. There are 2 types of invocations:
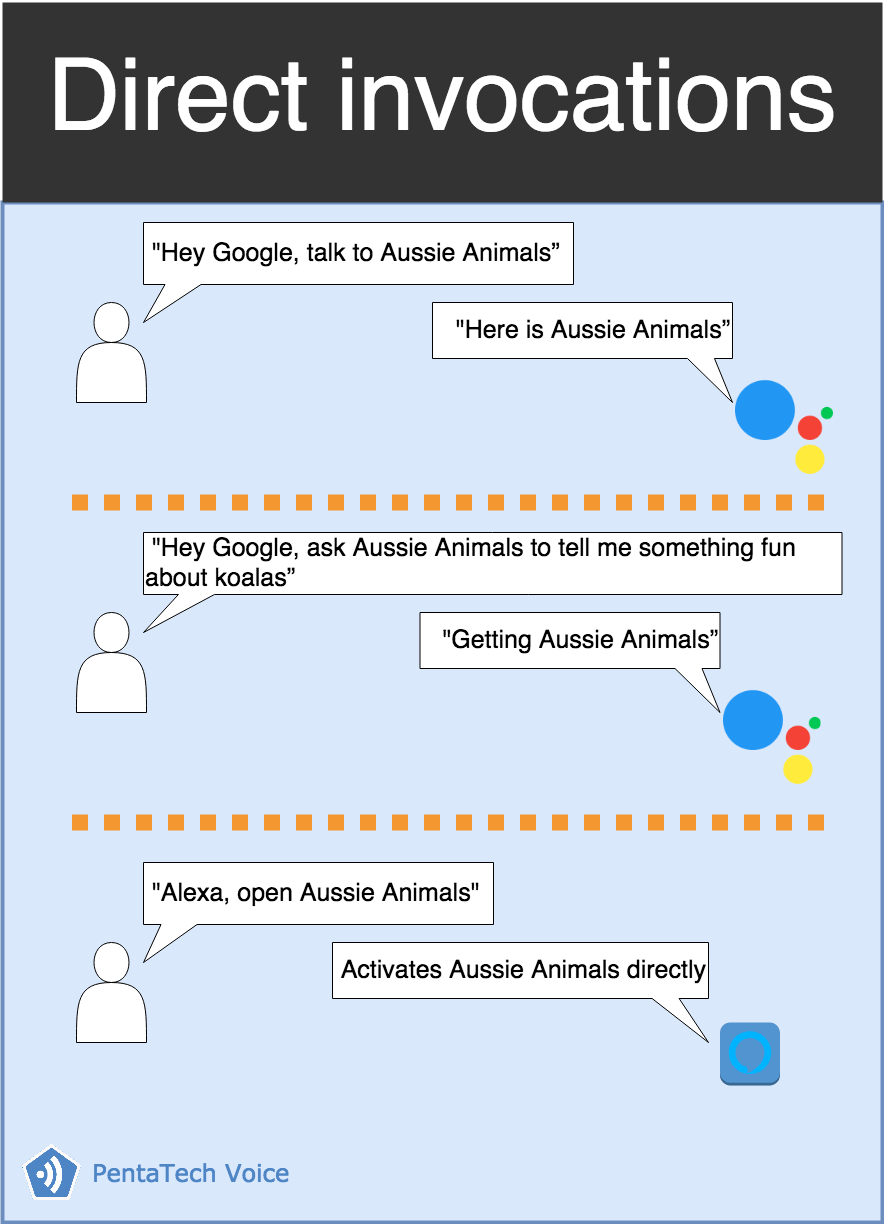
Direct invocations
In some cases the request is direct or explicit, this means that the user specifically calls out the name of the voice application that they want to engage with. In this instance, the platform will simply activate the voice application. Google Assistant calls it explicit invocations meanwhile Amazon Alexa refers to this as named invocations.
Let’s have a look to some examples:
Indirect invocations
The other scenario is when the user asks for something they need however, they do not specify which application will resolve their need. The voice-activated device may recommend to users what is the best available way to respond to their query. Google Assistant calls it implicit invocations meanwhile Amazon Alexa refers to this as name-free interactions.
Let’s have a look to some examples:

Why is this relevant to your business?
Your customers may not know your business name or how to get it directly. Similar to searching for a term on Google search. On voice, you want to be the first one so the indirect or implicit invocation favours your business. This opens up a brand-new era of search optimisation on voice-activated devices.
Driving traffic to your voice application
Firstly, you need to have clarity around your voice strategy and how you intend to drive your customer attention to your voice app. Secondly, finding the gaps or unattended terms that are still available to be leveraged. Generating engaging and meaningful content will make a difference.
Final remarks
The following table summarizes the different options when it comes to direct and indirect interactions with voice-activated platforms:
| Direct | Indirect | |
| Google Assistant | Explicit invocation with or without specific request Example: “Hey Google, talk to Aussie Animals” | Implicit invocation Example: “Hey Google, tell me something scary about crocodiles” |
| Amazon Alexa | Named invocation with or without specific request Example: “Alexa, open Aussie Animals” | Name-free interactions Example: “Alexa, tell me something scary about crocodiles” |




